SINTEF’s Version on Fire Resistance Upgrade of Cultural Heritage Doors
Older wooden doors can be one of the weaker points with regards to fire resistance in apartment buildings.
When it comes to fire safety in apartment buildings, old wooden doors often represent a weak point. Starting from this consideration, SINTEF (Stiftelsen forindustriall og teknisk forskning, “The Foundation for technical and industrial research”) in collaboration with RISE Fire Research and NIKU (Norsk institutt for kulturminneforskning), published a guideline in 2022 that “presents possible solutions for the assembly of glazing, protective panels, sealing strips, door frames and door hardware when improving the fire resistance of old wooden doors with cultural heritage value.”
The Guideline (Fire Resistance Upgrade of Cultural Heritage Doors) deals with the intervention on the door itself in cases where this is necessary. The approach is based on small-scale fire tests and knowledge from previous experience.
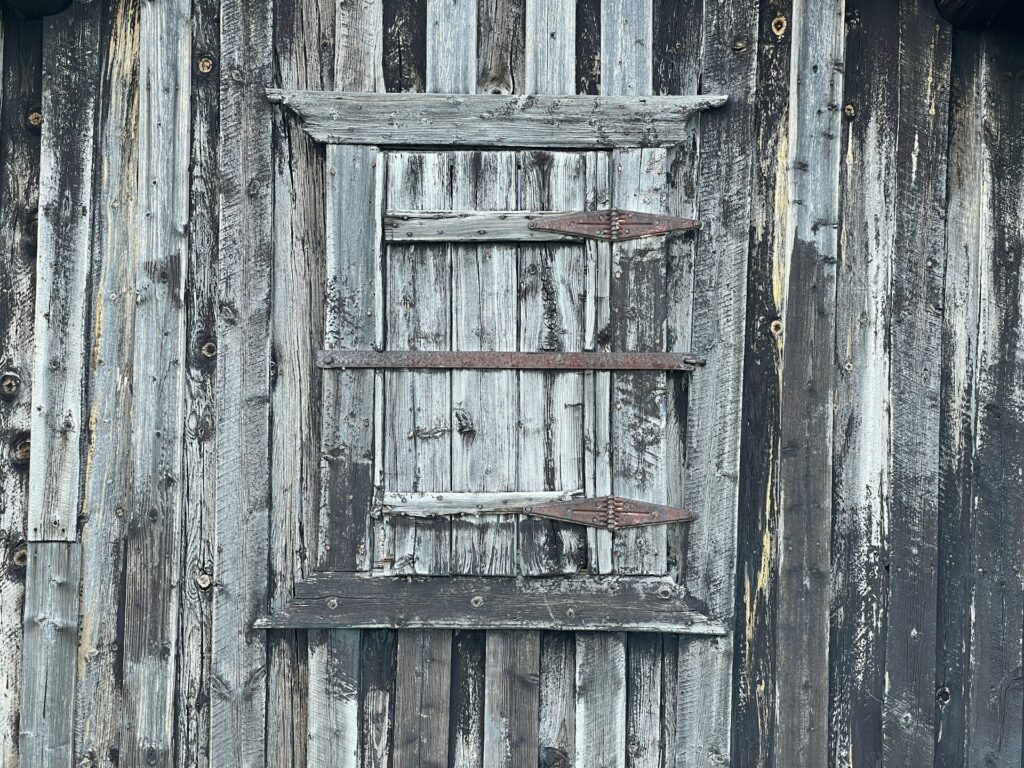

The strategy to improve the fire resistance of cultural heritage doors is defined by aiming to achieve a duration of approximately 30 minutes, similar to standard fire resistance tests. In general, this requirement is specifically aimed at situations where replacement of the door for historical or aesthetic reasons is not feasible or desirable.
The first result of the document, where older doors with a thickness of between 40 and 50 mm, consisting of a glass upper part and a thinner wooden door panel at the bottom, were considered, is that, to preserve its antiquarian nature, any changes should be minimally invasive and easily reversible. Additionally, four fire tests were conducted, each involving two models of small doors. Various methods for fitting fire glass, plasterboard and glazing strips were examined, leading to the following key findings:
- Fire-resistant glass must have a minimum rating of 30 minutes (both integrity and insulation) and should be securely fastened using steel frames or angles.
- Thinner components, such as fielded wooden panels, can be reinforced by incorporating stone wool and robust 12.5 mm gypsum boards.
- To enhance fire resistance, both intumescent strips and silicone gaskets must be applied around the door leaf.
- The gap between the door frame and the wall should be sealed using stone wool and fire sealant.
The guideline serves as a resource for ensuring the fire safety of older wooden doors in situations where maintaining historical integrity is a priority and replacement is not a viable option. The document is structured in three chapters:
- Background and premises
- Preservation of doors with cultural heritage value
- Guideline (3.1 Mounting of fire resistant glass; Mounting of protective boards; Mounting of sealing lists; Door frame; Door hardware).
The bibliography also includes the citation of the IFE (Institution of Fire Engineers) document “Guide to the history of fire-resistant wooden panel doors“